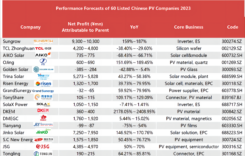
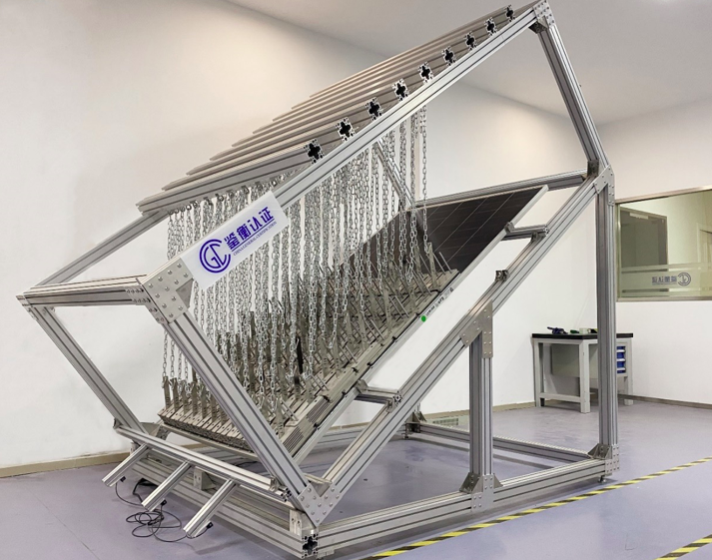
PVTIME – Trina Solar has successfully completed non-uniform snow-load testing at the CGC East China PV Testing Center with its new-generation Vertex 670W modules. Results demonstrated that the critical snow-load of the five modules tested exceeded 6,600 Pa, actually reaching 7,000 Pa, equivalent to the pressure generated by 2.8 meters of snow, much higher than conventional non-uniform snow-load norms. This represents proof of the excellent snow-load resistance of Vertex 670W, the strength convergence of the non-uniform snow-load testing reflecting the product’s consistently excellent quality.

The current path taken by PV modules is for increasingly high power and expanding size, which presents significant challenges for module materials, design and process and forces the upstream and downstream industry chain to set stricter requirements in terms of a module’s mechanical performance.
After passing the standard 5400Pa static mechanical and dynamic mechanical load tests, the Vertex modules continued to challenge non-uniform snow-load testing in order to more rigorously evaluate their performance in heavy-snow conditions.
Snow exerts uneven pressure when it accumulates heavily on a module’s surface, especially at the bottom of the module. The non-uniform snow-load testing specifically evaluates the ability of a module to withstand such uneven pressure when encountering heavy snow, thus more effectively circumventing snow pressure in areas with heavy snowfall causing module failure. This includes bent or broken frames, uneven backglass breakage and partial or complete disintegration of the installed system. In this way it is possible to provide an optimal solution for customers and owners.
In contrast to the dynamic and static load tests based on IEC 61215 and IEC 62782, IEC 62938:2020-based non-uniform snow-load testing is a standard procedure which can be considered as a risk control for differentiated application scenarios. It does so by simulating the module’s snow-load resistance in a real-world environment. Modules that pass this standard test exhibit two characteristic values: the value of snow load that accumulates on the surface when the module fails and the power attenuation value and electrical safety performance of the module under critical snow-load conditions.
The test data demonstrating the critical snow load for all five of Trina Solar’s modules to be as high as 6,600 Pa or more, with a maximum of 7,000 Pa, was much higher than the usual required norms for non-uniform snow loads. Based on an average snow density of 0.25g/cm3, this is equivalent to the pressure generated by 2.8 meters of snow unevenly pressing on the modules.
Combined with the ultimate load capacity of the Vertex 670 module and the standard introduction of a safety factor of 1.5 for the final snow-load test, module power attenuation was just 0.56%, demonstrating the product’s excellent snow-load resistance.