PVTIME – Despite suboptimal sunshine hours, Germany is still one of the largest solar power producers in the world. As of 2019, Germany ranks fourth in the world with its total installed capacity of more than 49 GW. Last year, Germany added nearly 4GW in solar capacity, which is a 30% growth from 2018. Although the annual target of the German Federal Government for PV expansion was exceeded, the goals of the energy transition for 2030 are still out of reach.
With the prevalence of the COVID-19 pandemic and uncertainty surrounding the 52GW cap, solar development in Germany in 2020 is a topic closely followed by numerous parties in and out of Germany.
Aiming to provide an informative and detailed update on how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected the German PV industry’s supply chain and business operations, PVTIME invited three PV industry veterans to its first English webinar “German PV Market COVID-19 Update” on July 29.
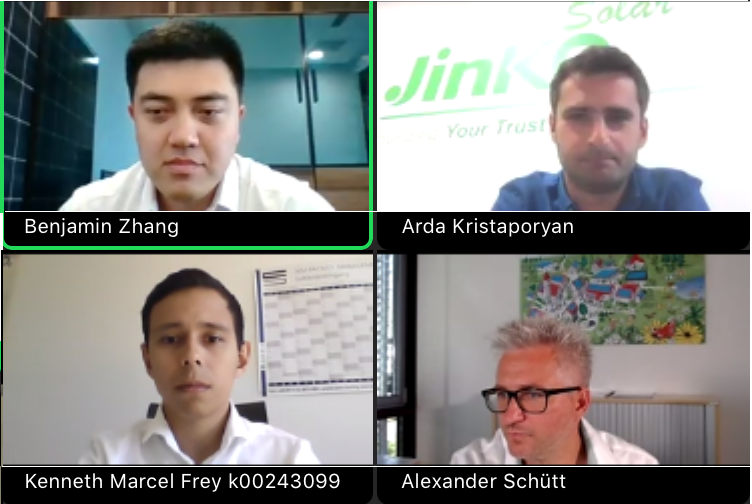
Arda Kristaporyan, Head of Sales Central Europe of JinkoSolar EU; Kenneth Marcel Frey, Executive Director of Huawei’s Germany Enterprise Digital Energy Business Department; and Alexander Schütt, Managing Director of BayWa r.e Solar Energy Systems GmbH, shared their unique perspectives and views on the current state of the German PV market as well as provided an outlook for the German PV market going forward.
The impact of COVID-19 and 52GW cap removal on solar development in Germany
In February, following the initial outbreak of COVID-19, production in China was physically not possible due to factory shutdowns. However, demand remained high for solar products and there was a huge back order in March due to uncertainty relating to the effects of the pandemic. Larger number of order were placed by buyers who wanted to avoid potential supply shortages. According to Arda Kristaporyan, Head of Sales Central Europe of JinkoSolar EU, in the end of February and beginning of March, COVID-19 caused a supply shortage in the EU. However, when production regained momentum in China, there was a noticeable reduction in global demand due to the virus outbreak. The lack of manpower, project financing, and approval of operation permits had a direct effect on the supply and demand balance, shifting the market from seller’s to buyer’s in a short time, leading to an upstream crash. Subsequently, significant price drops in wafers and raw materials came first, followed by a decrease in module prices.
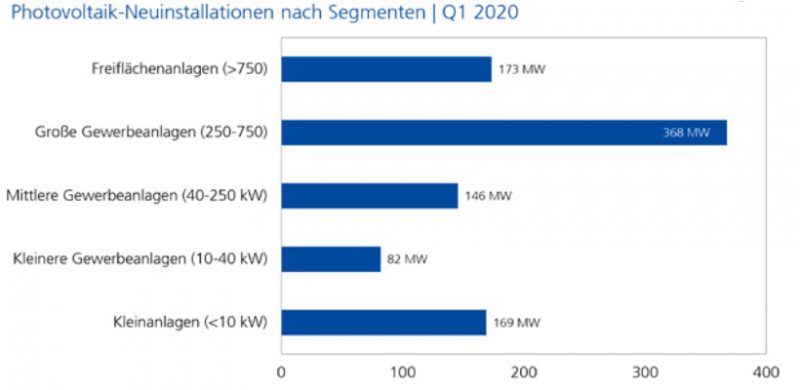
For the German market, the fear of COVID-19’s impact was in reality not as big as imagined, and the actual impact on the market was manageable. Commercial and residential projects were delayed or postponed due to the lack of manpower (increased labor costs), project financing, and approval of operation permits. Evidently, the residential segment was the most affected by the pandemic as homeowners were reluctant to have workers near their homes in order limit potential exposure.
In Q1 of 2020, Germany added 983MW in new installations. For comparison, 986MW was added in Q4 of 2019. It is anticipated that 4.5GW in new installations will be added by the end of 2020, and another 6-7GW will be added in 2021.
The pandemic accelerated the removal of outdated capacity in the market and provided an opportunity for leading industry players to expand their market shares. Having shipped 3.4GW globally in Q1, JinkoSolar’s annual shipment target of 18-20GW for 2020 remains unchanged. With the resumption of delayed projects and increase in global demand, JinkoSolar’s shipment numbers in the second of 2020 will be even better. In Huawei’s case, despite of COVID-19, overall revenue for the first half of 2020 exceeded 64 billion USD with net profit of 9.2%, which is a 13.1% increase year-on-year.
In Germany, the removal of the 52GW cap will prove to have a bigger impact than the COVID-19 pandemic. Without the removal, the 52GW limit would have been likely reached by mid-2020, leading to the collapse of the German PV market and PV systems with low self-consumption rates in particular. With the cap lifted, the German PV market can now continue its 300-450MW per month growth. Moreover, the market for PV systems up to 750kWp will continue to expand like it has for the past several months while systems beyond 750kWp will need to participate in cost completive auctions.
AI boost fighting COVID-19
As countries around the globe grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic, Huawei is aiding the battle against COVID-19 with the help of tools like 4G, 5G, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, helping to prevent, diagnose and treat the disease, while supporting scientists look for a cure. ICT isn’t just a crucial tool for combating the virus, but also an engine for economic recovery. According Kenneth Marcel Frey, Executive Director of Huawei’s Germany Enterprise Digital Energy Business Department, the production of inverters has been fully restored while the supply chain and logistics have been operating normally since March.

For Huawei, the health and safety of its employees is their top priority. Huawei’s local teams have been able to work remotely and if onsite services are needed, adjustments in team management are been made to ensure that the health and safety standards are in line with the constantly evolving regulations of different countries. In light of COVID-19, Huawei has also made its Online Smart I-V Curve Diagnosis to its customers free of charge for three months, allowing them to inspect their plants remotely.
The cancellation of offline industry events such as Intersolar Europe made the showcasing of new products in the physical form rather difficult, leading JinkoSolar, Huawei, and BayWa r.e to develop more active presences online, doing much of their employee/customer training, communication, and promotion in the form of online initiatives such as webinars and virtual showrooms. Particularly, Huawei launched its Smart PV Community in March of 2020, offering online lessons and the latest information on its products and solutions.
Trends, driver, and challenges
In terms of trends and drivers, regardless residential or commercial, self-consumption and the desire to be socially responsible are huge drivers for the end-consumer market in Germany. Residential storage systems are becoming standard in Germany and modules efficiency is a crucial factor when consumers are selecting their residential systems.
According to Alexander Schütt, Managing Director of BayWa r.e Solar Energy Systems GmbH, there are several challenges for the German PV market going forward. The first being the low target of only 2.5GW within the current EEG. In order to meet the 2030 Paris Agreement goal, the target would need to be uplifted to 5-10GW annually. Secondly, there are still existing parties that are working on hindering the adoption of renewable energy and the removal of self-consumption, self-consumption as a driver needs to be strengthened and supported. Last and not least, there are currently not enough installers to support the rate of growth in Germany and backlogs of installation orders from 3-6 months is quite common. To a certain extent, this is definitely a factor hindering the growth of the residential sector in Germany.

For more information and access to the Q&A portion of the webinar, the complete recording of German PV Market COVID-19 Update is available at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f22CXMGfyb4&feature=youtu.be