PVTIME – The year 2024 is poised to be a transformative year for the global photovoltaic industry, characterised by substantial innovation and expansion.In China, prominent module manufacturers have announced ambitious production capacity targets, with a considerable volume of shipments to the global market intended to expedite the deployment of solar power.
A comprehensive analysis of global module shipments from 24 prominent Chinese solar module manufacturers reveals that shipments are projected to range from 600GW to 650GW, signifying a new zenith in the past decade. This figure stands in stark contrast to the anticipated global installed capacity of PV solar, estimated to be between 593GW and 600GW in 2024.
It is important to note that not all companies have yet reported their full annual shipment data, and therefore the data presented here may not be conclusive. It should be regarded as a provisional estimate, subject to final announcement of company data.
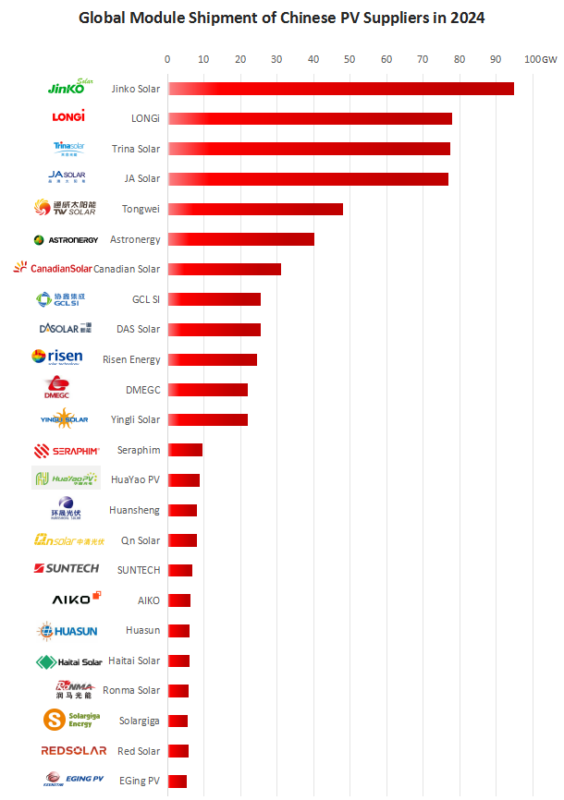
JinkoSolar has sustained its position at the forefront of the industry, with module shipments exceeding 90GW.In the initial three quarters of 2024, approximately 68GW of solar cells were shipped, with 23.8GW shipped in the third quarter alone. JinkoSolar is anticipated to ship approximately 22-32GW of solar modules in the fourth quarter. Presently, JinkoSolar’s n-type shipment ratio stands at 90%.By the conclusion of 2024, the company’s wafer, cell and module production capacity is projected to reach 120GW, 95GW and 130GW, respectively, with a module efficiency of 26.5%.
In October 2024, the company announced its intention to issue no more than $4.5 billion in offshore GDRs, a move that is expected to be of significant benefit to its 1GW high-efficiency module factory in the US, its production base for its 14GW integration project in Shanxi, China, and its additional working capital or loan repayment.The company’s 2025 shipment target has not yet been disclosed; however, its strategy to secure its leadership position is expected to remain unchanged.
With an estimated annual global module shipment of 76GW to 80GW, LONGi is the PV giant and is ranked second on the list.In the first three quarters of 2024, LONGi shipped 51.23GW of modules, of which 13.77GW were BC modules, representing an increase of 17.70% over the same period last year.
The company has recently achieved a significant breakthrough in HPBC2.0 technology, with cell efficiency reaching 26.6%, module conversion efficiency rising to 24.43%, and double-sided rate exceeding 70%. By the end of 2025, LONGi aims to achieve 70GW of BC battery production capacity, with HPBC2.0 contributing approximately 50GW. Furthermore, by the close of 2026, the company’s production facilities in China will undergo an upgrade to facilitate the delivery of BC products.The introduction of cost-effective metal solutions in BC production lines is expected to contribute to a reduction in manufacturing expenses.In comparison, Trina Solar is anticipated to have shipped approximately 77GW of solar modules in 2024, marking a substantial increase from the 60GW shipped in 2023.
JinkoSolar continued to lead the way, unsurprisingly maintaining its position with module shipments of over 90GW. In the first three quarters of 2024, about 68GW of solar cells were shipped, with 23.8GW shipped in the third quarter, and JinkoSolar is expected to ship about 22-32GW of solar modules in the fourth quarter. Currently, JinkoSolar’s n-type shipment ratio is 90%.
Trina Solar’s R&D investment amounted to 4.3 billion yuan during the initial three quarters of 2024, with 1.597 billion yuan allocated to R&D in the third quarter alone.On 4 December 2024, Trina unveiled its latest generation of i-TOPCon Ultra technology n-type solar module products. The large version of this module has a power rating of up to 760W, with a conversion efficiency of 24.5%, while the medium version has a power rating of up to 670W, and the small version has a power rating of up to 495W, with an increase in module efficiency of 1.8%. The full implementation of these upgraded products is scheduled to occur in the second quarter of 2025, with an initial supply capacity target of 10GW in the first phase.
In order to mitigate risks from changes in the global trade environment and to maintain Trina Solar’s leading position in highly profitable markets, Trina Solar has commissioned facilities in Indonesia with a capacity of 1GW of cells and 1GW of modules and in the US with a capacity of 5GW of modules in the second half of 2024. In a related development, FREYR Battery (NYSE: FREY), a US-based solar manufacturer, has completed the acquisition of Trina Solar’s US solar manufacturing assets. This includes a 5GW solar module plant in Wilmer, Texas, which commenced production on 1 November 2024 and is projected to attain full capacity by the second half of 2025. A significant aspect of this acquisition is the presence of long-term offtake agreements with US customers, which are expected to contribute to 30% of the planned production capacity.
JA Solar is estimated to have shipped between 75GW and 79GW of modules in 2024, with 57GW shipped in the first three quarters of the year and a further 22GW shipped in the last quarter. This places JA Solar as the world’s second largest module manufacturer in terms of shipments.
By the close of 2024, JA Solar’s manufacturing capacity for wafers, cells, and modules was 80GW, 80GW, and 100GW, respectively, with an n-type capacity of approximately 70GW. The company’s latest n-type Bycium+ cells have demonstrated a conversion efficiency of 26.5% in mass production.
JA Solar’s manufacturing costs had already undergone a substantial reduction, and the enterprise had become profitable for the first time, with a stable and healthy operating cash flow. It is anticipated that the company will continue to demonstrate an upward trend in net profit in 2025 and 2026.
It is disclosed that Tongwei Solar, the leading manufacturer of silicon materials and solar modules, shipped 45-47GW of modules in 2024, representing a year-on-year growth of approximately 50%, with 15-17GW shipped in the fourth quarter of 2024, also demonstrating a year-on-year growth of about 50%. In the past year, Tongwei Solar has been engaged in expanding its domestic and overseas channels, which will lead to sustained and high growth of module business scale in the future.The R&D strength of Tongwei Solar’s TOPCon products has once again reached a record high. The positive power of Tongwei Solar’s G12-66 and G12R-66 versions of TNC modules reached 763.4W and 663.5W, respectively, as a result of the continuous innovation of tube-type PECVD poly deposition, poly finger, EPT passivation, fine line printing and other technologies.
The substantial increase in module shipments by Astronergy (Chint) is particularly noteworthy, with a growth trajectory from 28GW in 2023 to over 40GW in 2024. Within China, Astronergy shipped 26.1GW, accounting for 65% of the total, while 14.1GW was shipped to the overseas market, accounting for 35%.
Astronergy boasts a production capacity of at least 53GW of cells and 55GW of modules utilising TOPCon technology, with all ten production sites located in China and Thailand demonstrating seamless operational efficiency. Notably, Astronergy stands as the sole entity within the PV industry to have accomplished ZBB technology implementation in TOPCon processing within mass production. The company’s products are gaining recognition in the European market, leading to an expansion in solar production utilising ZBB technology. The target is to achieve a production capacity of 20GW by the end of 2025. In comparison, Canadian Solar’s solar module shipments in 2024 were approximately 31GW. By the close of 2023, Canadian Solar had increased its target for module shipments in 2024 to between 42GW and 47GW, though this was subsequently adjusted to between 32GW and 36GW in order to maintain profitability.
Canadian Solar has shifted some of its attention from solar modules to energy storage solutions. From January to September 2024, Canadian Solar achieved module shipments of 22.9GW, of which 8.4GW were shipped in the third quarter, representing a 2.4% sequential increase. Concurrently, shipments of its large-scale energy storage products reached 4.4GWh, with full-year shipments expected to be 6.5-7.0GWh, and further increases anticipated in the fourth quarter. The company’s commitment to technological advancement is underscored by its dedicated research and development team, which as of 30 September 2024, had submitted a total of 4,761 patent applications, with 2,242 of these applications being classified as key patents.
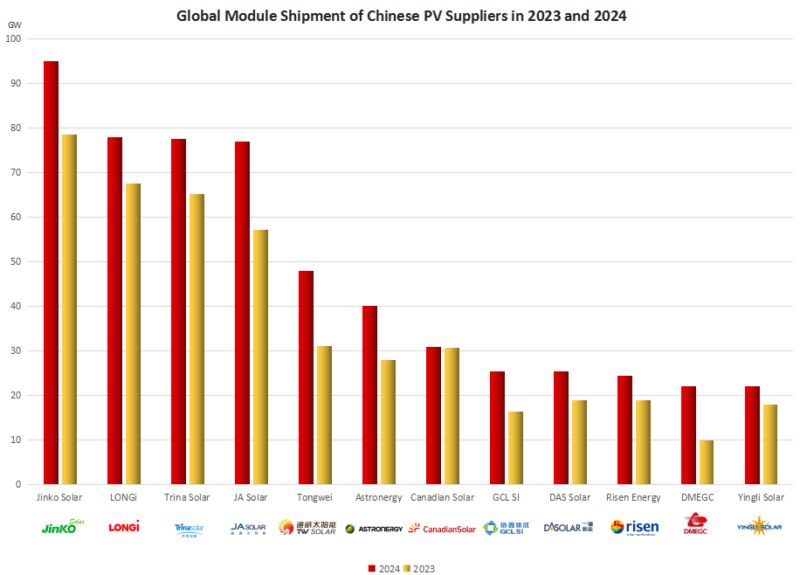
In 2024, both GCL SI and DAS Solar attained global solar module shipments of approximately 25GW to 26GW. GCL SI maintained a high capacity utilisation rate within the industry, with its solar cells and modules operating at near full capacity, resulting in robust production and sales performance. The company has established a substantial production capacity, with 30GW dedicated to high-efficiency large-size module manufacturing and an additional 14GW allocated for TOPCon cell production.It is noteworthy that GCL SI and JinkoSolar are the only two companies among the top 10 global leaders in solar module shipments that have achieved profitability in 2024. From January to September 2024, GCL SI’s gross profit margin stood at 10.1%, 7.6%, and 11.4%, in that order.
The company’s advanced module production capacity is entirely based on 182 and 210 large-size high-efficiency crystalline silicon modules, compatible with TOPCon and HJT cell technology, and reserved for perovskite and crystalline silicon tandem modules and other product development interfaces. On 26 December 2024, GCL SI unveiled GPC2.0 high-efficiency modules employing BC technology, which augmented the power of the 2382*1134mm module to 660W. Furthermore, on 12 June 2024, GCL SI unveiled its innovative carbon chain SIRO modules, which integrate blockchain digital technology with granular silicon low-carbon technology, thereby enhancing the carbon control and reduction effects across the PV industry chain.
DAS Solar, a frontrunner in n-type PV technology, shipped approximately 26GW of solar modules in 2024.The overseas market expansion of DAS Solar has been rapid, with the company entering the TOP list within a few years.
This expansion can be attributed in part to the provision of technical support from TOPCon, with concurrent advancements in DBC, TSiP, SFOS and other technology routes contributing to DAS Solar’s achievements. Notably, all innovative technologies have met their expected milestones, with a target efficiency of 40% to be achieved in near future. By the conclusion of 2024, DAS Solar attained a production capacity of 40GW of solar cells and 40GW of modules per annum, signifying a substantial augmentation from the 30GW of each in 2023.
Risen Energy anticipates the shipment of approximately 24.5GW of solar modules in 2024, with 5GW of these being HJT modules. This signifies a substantial increase from the 19GW shipped in 2023.The company’s module shipments during the initial three quarters amounted to 14.6GW, indicating a consistent progression.
The company’s most recent advancements in HJT cell technology, which boast an average conversion efficiency of over 26%, with a recorded efficiency of 26.5%, are of particular note. The output power of its mainstream module has surpassed 710W, with plans to enhance this to over 720W. In addition, Risen Energy has recently announced its expectation to deliver mass-produced HJT Hyper-ion Pro modules with a power of 730W in the first quarter of 2025.
DMEGC and Yingli Solar both achieved global solar shipments of more than 22GW in 2024. It is noteworthy that the shipment volume of these companies is approaching that of GCL SI, DAS Solar and Risen Energy, and it is anticipated that it will soon exceed their shipments.
The preeminence of Chinese PV companies within the top ten list is primarily attributable to their cost-effectiveness, which is attributable to the integrated nature of China’s PV industry.The nation boasts an unparalleled dominance over the four primary manufacturing segments: silicon, silicon wafers, cells and modules. This integrated industry chain enables Chinese PV companies to achieve cost-effectiveness in production, consequently ensuring their price competitiveness in the global market. In contrast, manufacturers in other countries face considerable challenges in competing with the Chinese PV industry, with the exception of large-scale local manufacturing incentives and trade restrictions on imports.Furthermore, the average selling price (ASP) of various module types has decreased to below 10 cents per W, marking a pivotal moment for the global PV industry.Chinese PV companies are strategically positioned to compete in price markets due to their ability to effectively manage costs.
The other module manufacturers on the list, which are expected to ship between 5.2GW and 10GW in 2024, are engaged in fierce competition with each other.In the midst of market turbulence and prices reaching a nadir, module manufacturers have been able to maintain their focus on increasing shipments and consolidating their market position.The investment and achievements of Chinese PV companies in technology R&D have established a benchmark for technological innovation in the global PV industry. In response, other countries and enterprises have followed suit, thereby driving the technological progress of the entire industry.For instance, the development and application of advanced technologies such as TOPCon and BC have improved the conversion efficiency and performance of PV modules and enhanced the competitiveness of PV power generation.