PVTIME – A recent empirical project led by Inner Mongolia Energy Group in China has demonstrated remarkable results in a photovoltaic (PV) desert control project. Spanning approximately 1,533 hectares, this project conducted the first performance comparison between LONGi’s HPBC2.0 technology—Hi-MO 9 modules—and conventional TOPCon modules in a sandy environment. The study offers valuable data to guide future PV technology selection and project deployment in desert regions.

Located in an area with about 3,000 hours of annual sunshine, the project site also faces harsh continental climate conditions such as drought, scant rainfall, high evaporation rates, and frequent sandstorms. These conditions place extreme demands on the reliability and long-term power generation performance of PV equipment. Under identical environmental and site conditions, 640W BC modules and 575W TOPCon modules were installed for a direct comparative assessment.
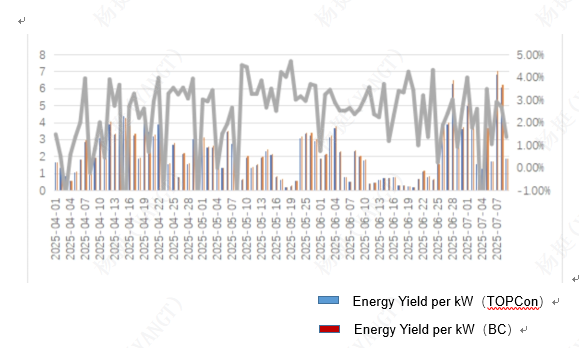
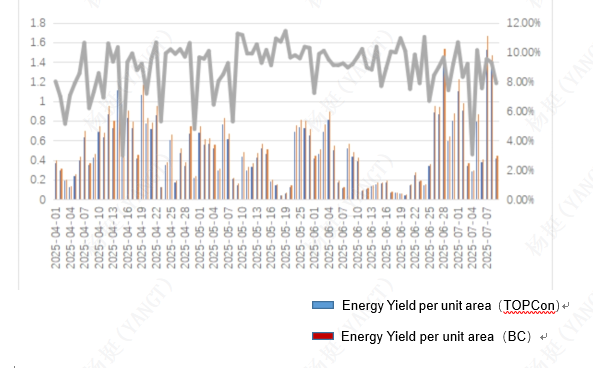
Data gathered from April to July 2025 showed that LONGi’s BC technology significantly outperformed TOPCon, registering a 2.45% increase in electricity generation per kilowatt and a 9.05% rise in power output per unit area. Particularly noteworthy was BC’s performance in June—a month with 14 overcast or rainy days—where it consistently outperformed TOPCon modules across all 30 days. The monthly cumulative power generation gain reached 2.44%, underscoring BC’s superior efficiency under low-light conditions.
The adoption of BC technology not only provides critical guidance for large-scale PV desert control projects but also sets a technical benchmark for renewable energy development in desert and arid regions. These findings highlight that high-efficiency BC technology can significantly enhance the lifecycle value of PV power stations and support sustainable energy development in desertified areas characterized by dry, low-rainfall conditions.

Scan the QR code to follow PVTIME official account on Wechat for latest news on PV+ES